13. BioActive Conformations:
Bioactive Conformations and
Pharmcophores
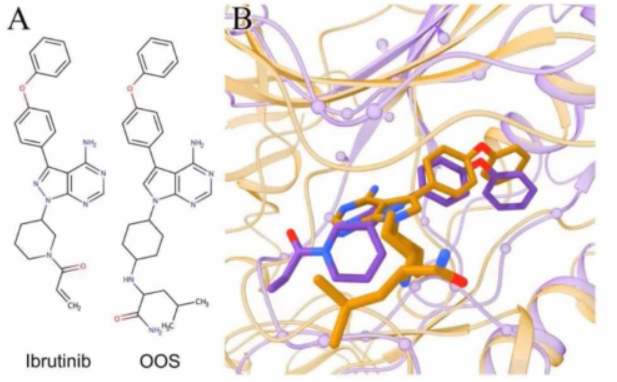
X-ray Structures of Complexes
Protein-ligand complex structures show bioactive
conformations.
The ligands' bound state, or "binding mode," has biological activity.
Bioactive ligand conformations are utilized in ligand-based drug design
to find more active molecules.
X-ray Structures of Complexes
To identify more active substances, bioactive
ligand conformations are used.
Drug design based on ligands (LBVS)
-
3D database search
-
Modeling/searching of pharmacophores
Pharmacophore
It is described as the spatial configuration of atoms or groups in a molecule that is essential for its bioactivity.
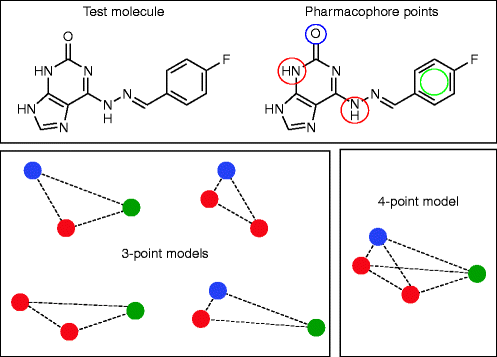
Pharmacophore Features
Consists of all
inter-feature distances and three or four pharmacophore characteristics.
Six inter-feature distances and four characteristics define a 4-point
pharmacophore.
Features are defined to take into consideration the chemical properties that various atoms and groups represent:
-
donors or acceptors of hydrogen bonds.
-
groupings that are negatively or positively charged.
-
hydrophobic molecules.
-
centers of aromatic systems or rings.
6 common pharmacophore characteristics
Structure-based Pharmacophore
Pharmacophore characteristics are chosen from X-ray structures to represent significant protein-ligand interactions.
Pharmacophore searching
Four features and six spacing between the
features make up a four-point pharmacophore.
An encoded pharmacophore model searches 3D databases for more substances
that share the same pharmacophore.
Potential candidates are database molecules with
the same pharmacophore but distinct core structures (hits)
Inter-feature distances are encoded as short distance ranges when
searching to prevent the search from being overdetermined (no hits)
Structure-based Drug Design
requires in-depth understanding of the
three-dimensional ligand binding site.
attempts to represent ligands that are highly complementary in terms of
shape, structure, and chemical makeup to the receptor site.
Pharmacophore-based Design
Find potential compounds by comparing them to a
predetermined pharmacophore that "mimics" known actives.
The approach resembles 2D similarity searches based on molecular graphs.
While 2D pharmacophores can also be defined, the information content of
bioactive conformations is higher.
Unknown Bioactive Conformation
Only a small portion of pharmacological targets
have known bioactive conformations based on X-ray structures.
When using the pharmacophore idea, binding conformations of active
chemicals must be modeled if they are unknown.
Pick at least two well-known active substances.
To sample low energy conformations, do a systematic conformational
search with energy minimization.
Conformational Sampling
Look for low-energy conformations on a compound's potential energy surface.
Pick at least two well-known active substances.
Conduct a systematic search for conformations, sampling low-energy
conformations.
Find the two active chemicals' sampled minimal energy conformations.
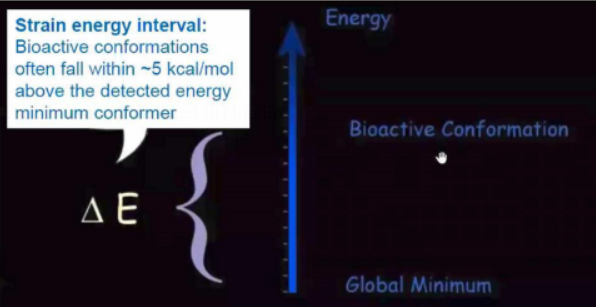
Choose every conformer that falls within a 5 kcal/mol energy range with
respect to the minimum.
Strain Energy upon Binding
Global minimum conformations are often not those
that are bioactive.
Strain energy is present in bound ligands as a result of (induced fit)
binding.
Pick at least two well-known active substances.
Sample low-energy conformations and conduct systematic conformational
search.
Identify the conformation with the lowest energy.
Choose every conformer that is 5 kcal/mol or less from the minimum.
Comparing the chosen conformers for the two active substances
methodically (superposition)
Pick the pair or pairs of conformations that are most comparable.
Comparison of Confomers
Comparison of the active compound A and B's low-energy conformations pairwise.
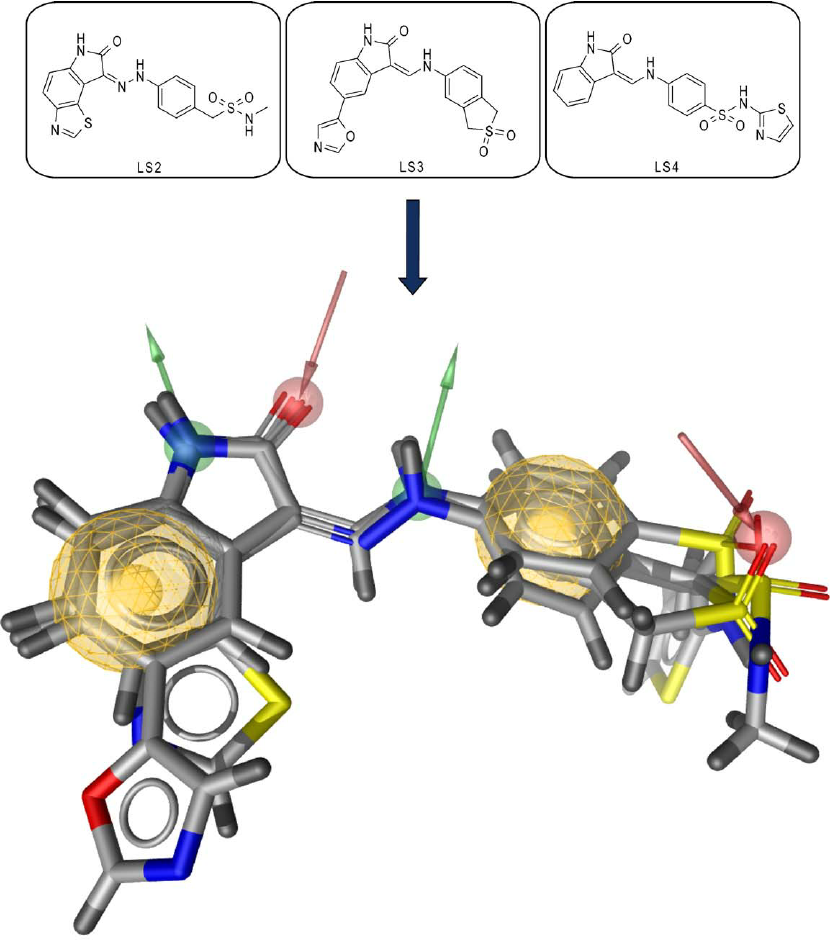
The bioactive conformations are probably represented by the conformers that are the most comparable.
Similar pharmacophores and binding modalities
Modeling Bioactive Conformations
Pick at least two well-known active substances.
Sample low-energy conformations and conduct systematic conformational
search.
Identify the conformation with the lowest energy.
Choose every conformer that is 5 kcal/mol or less from the minimum.
Comparing the selected conformers systematically.
Choose the most comparable pair(s) of conformations as the most likely
bioactive conformations.
---- Summary ----
As of now you know all basics of all the laws of thermodynamics.
-
Structure Based Drug Design
-
Pharmacophore Based Drug Design
-
Bioactive conformations
-
etc..
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________

________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
